The European institutions
The European institutions aim to ensure the functioning of the European Union and enable it to carry out its tasks.
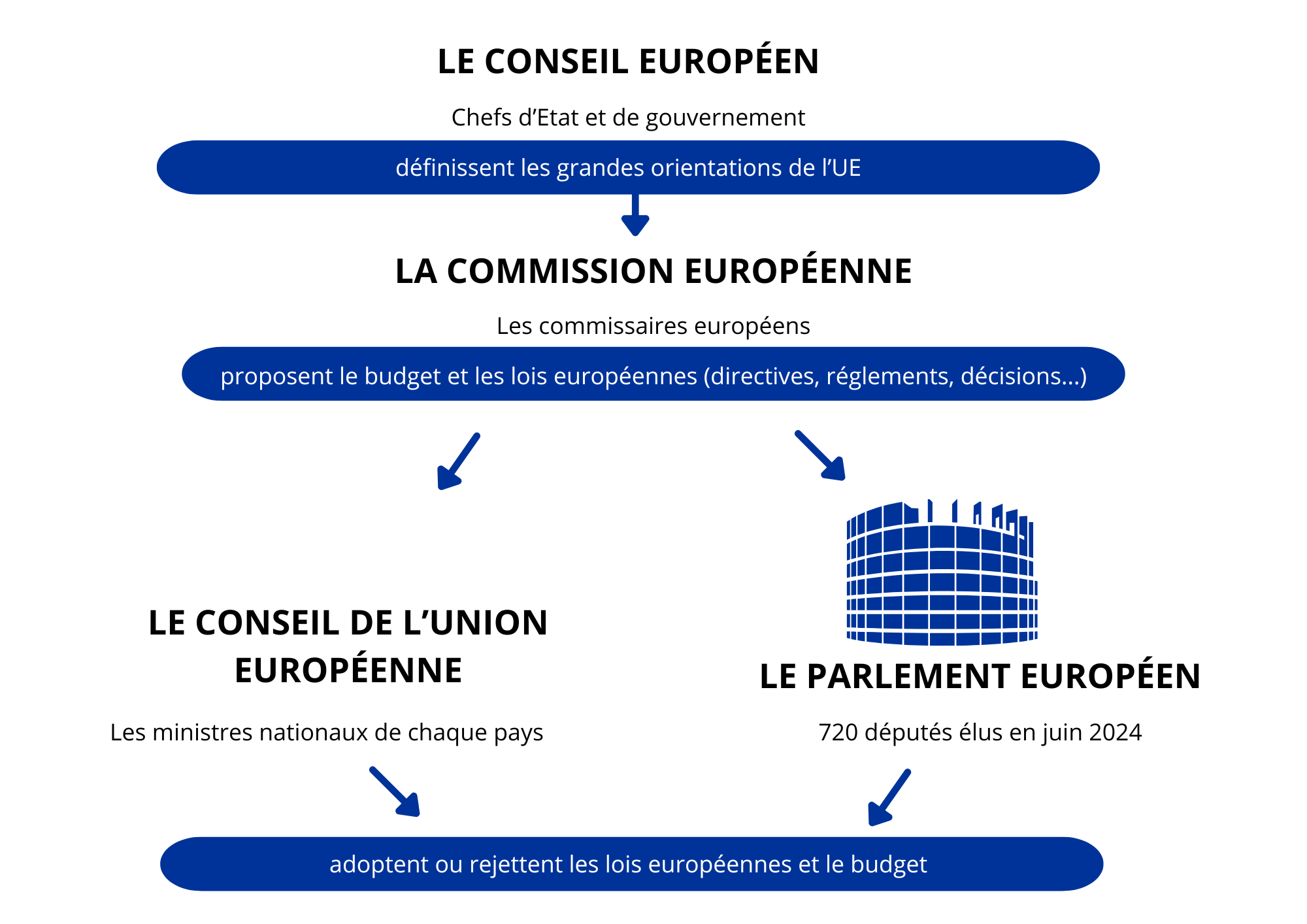
An institutional triangle
The institutional framework of the European Union is unique in the world and confers on everyone a role and powers of their own. In the institutional organisation of the European Union
:
- The EU's main priorities are set by the European Council, which brings together Heads of State and Government and European leaders.
- The interests of the EU as a whole are defended by the European Commission, whose members are appointed by national governments.
- The interests of the Member States are defended by the ministers of each country within the European Union Council.
- The citizens of the EU are represented by the 720 deputies, elected by direct universal suffrage. European Parliament.
It's in this institutional triangle – Commission, EU Council, European Parliament – what will be defined European policies and laws that will then apply throughout the European Union.
The European Council
The European Council meeting at Brussels on 27 Heads of State or Government of the Member States. He decides on the big Guidelines and priorities European Union policies but do not adopt legislative acts.
He intervenes to unlock a crisis situation, to resolve disputes between Member States or between different institutions. It defines the common foreign and security policy, taking into account the EU's strategic interests and defence implications.
He appoints and appoints candidates for certain high positions in the EU, such as the Presidency of the European Central Bank and the Commission.
Do not confuse it with the Council of the European Union or the Council of Europe.

The European Council is composed of the Heads of State and Government of the Member States of the European Union.
European Commission
The EU's Executive Body, the European Commission plays a key role in the preparation and implementation of European policy and owns the power of legislative initiative. It is therefore responsible for drawing up proposals for European laws which are subsequently submitted to the vote of the Council of the European Union and the European Parliament.
It manages EU policies and allocates European funding. The Commission shall establish the EU's budgetary priorities, in collaboration with the Council and Parliament, and shall monitor how the funds are used under the supervision of the Commission. Court of Auditors.
It shall ensure compliance with European law. Together with the Court of Justice, the Commission ensures the correct application of European legislation in all EU Member States.
It represents the European Union in the world. The Commission is speaking on behalf of all EU countries in international organisations, particularly in the areas of external trade and humanitarian aid. It also negotiates international agreements involving the EU.
The Political direction is provided by a team of 27 European Commissioners (one per country), led by President of the Commissionwhich decides on the allocation of responsibilities.
The day-to-day management of the Commission's affairs is carried out by its staff (lawyers, economists, etc.), which is organised into services called « Directorates-General» (DG). Each DG is responsible for Specific policy area.
The European Parliament
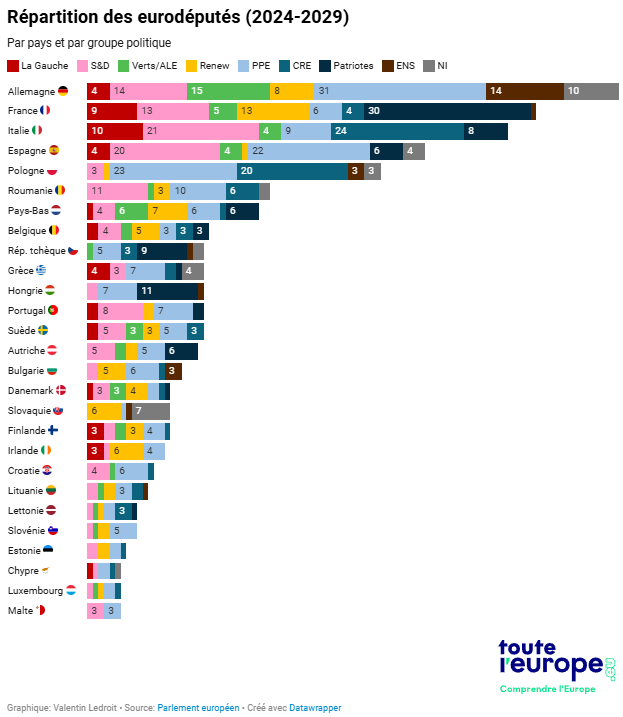
The European Parliament represents the 449 million European citizens. It is now the only European institution whose members are directly elected by direct universal suffrageEvery five years. Parliament has three main roles:
Legislative role
adopt Union legislation jointly with the Council of the European Union, on the basis of proposals from the European Commission. It decides on international agreements.
Monitoring role
it exercises democratic control over all the institutions of the Union. It elects the Chairman of the Commission and may vote on a motion of censure, obliging the Commission to resign.
Budgetary role
It shall draw up and approve the Union budget, together with the Council of the European Union.
He has his Strasbourg where he organizes his plenary sessions once a month over 3 to 4 days.
As in the French National Assembly, MEPs, elected for five years, are organised in European political groups. Each group appoints a group coordinator to decide how the group should vote in Parliament. However, no Member is bound by this decision and there is no official sanction induced by a vote different from that determined by the group.
Members cannot be members of several groups at a time. On the other hand, they may not belong to any group: they are then called the « Non-registered ». French political parties are affiliated with European groups.
Council of the European Union
Council of the European Union represents and defends the interests of the Member States EU. It brings together ministers from the 27 EU countries, but its composition varies according to the subject under discussion. Thus, if the Council is to discuss agricultural issues, it is the Agriculture Ministers who will meet.
The Presidency of the EU Council is held in turn by the EU countries for a period of 6 months.
The EU Council has five main responsibilities:
- He negotiates and adopts EU legislation with the European Parliamenton the basis of the proposals submitted by the European Commission.
- He coordinates policies of EU countries.
- It develops the foreign and security policy EU guidelines European Council.
- It concludes Agreements between the EU and other countries or international organisations.
- It adopts the EU annual budget the European Parliament.
Votes in the EU Council are generally taken by qualified majority, i.e. 55% of countries (15 out of 27) representing at least 65% of the total EU population.
Certain subjects such as foreign policy, EU enlargement, taxation and the multiannual budgetary framework require unanimous vote. In this case, only one country may block the adoption of a text.
Legislative role
adopt Union legislation jointly with the Council of the European Union, on the basis of proposals from the European Commission. It decides on international agreements.
Monitoring role
it exercises democratic control over all the institutions of the Union. It elects the Chairman of the Commission and may vote on a motion of censure, obliging the Commission to resign.
Budgetary role
It shall draw up and approve the Union budget, together with the Council of the European Union.

The Council Presidency is rotating and held every six months by a new EU member country.
The «Capital» European Union
Press regularly associates « Brussels » and the European Union while the Union has bodies in other Member States.
We can hold back. 4 cities « capitals in the EU » Brussels, Strasbourg, Luxembourg and Frankfurt.
Frankfurt, economic capital :
In 2007, the Treaty of Lisbon also recognised the European Central Bank (ECB) as a fully-fledged EU institution that defines and implements euro area monetary policy. And it is in Germany, the first European economic power with a very strong influence on monetary policy, that its seat is located.
Strasbourg, parliamentary capital :
the Alsatian capital is officially the seat of the European Parliament, the 12 annual plenary sessions bringing together all 720 MEPs.
Luxembourg, judicial capital :
While Luxembourg had been chosen in 1952 to temporarily host the European institutions, Brussels was the one that recovered the largest share of the cake in 1965. As compensation, the Grand Duchy retains the Secretariat-General of the European Parliament and European Court of Justice (CJEU). In 1977 the European Court of Auditors also settles in Luxembourg. It is the Union's independent external audit institution.
Brussels, Executive Capital:
the European Commission, the EU Council and the European Council. European Parliament special case In Brussels, the work of parliamentary committees is carried out, facilitated by proximity to the Commission and the EU Council.
Some extraordinary plenary sessions of the European Parliament are also held in Brussels.